Navigating the Complex Parts of Injection Molding Technology: A Comprehensive Guide
Time:
2025-04-14 11:00
Source:
Navigating the Complex Parts of Injection Molding Technology
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Injection Molding Technology
- Key Components of Injection Molding
- Understanding Mold Design in Injection Molding
- Types of Plastic Materials Used in Injection Molding
- The Injection Molding Process Explained
- Recent Advancements in Injection Molding Technology
- Applications of Injection Molding in Various Industries
- Challenges in Injection Molding and How to Overcome Them
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction to Injection Molding Technology
Injection molding technology is a dominant process in the world of manufacturing, specifically for creating plastic parts. This method allows for the mass production of intricate designs with high precision, making it a preferred choice for various industries. Understanding this technology involves delving into its core components, processes, and innovations that continuously shape its evolution.
Key Components of Injection Molding
In injection molding, several key components work together to produce high-quality parts. These include:
1. Injection Unit
The injection unit is responsible for melting the plastic and injecting it into the mold. It comprises a hopper for feeding raw material, a barrel for melting, and a screw for injecting the molten plastic.
2. Clamping Unit
The clamping unit holds the mold in place during injection. Its primary function is to ensure that the mold remains closed tightly as the plastic is injected, preventing any material from escaping.
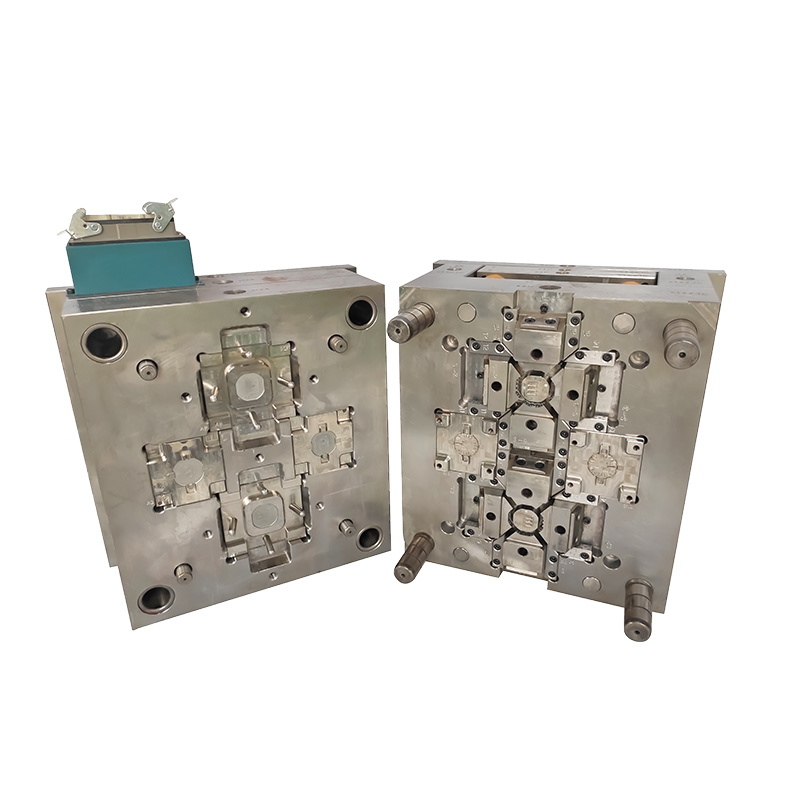
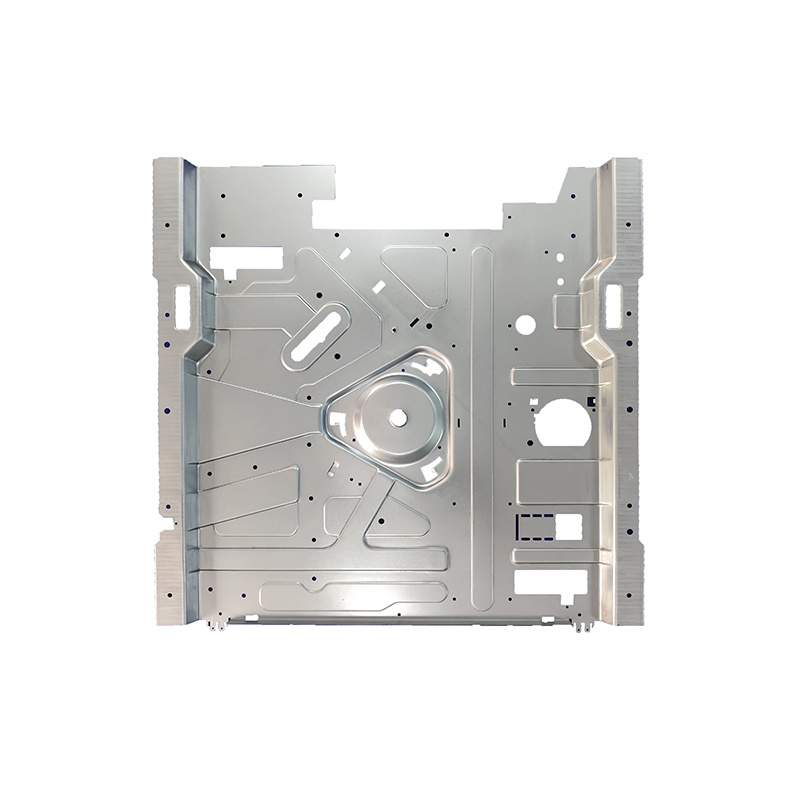
3. Mold
The mold is the heart of the injection molding process. It is typically made from metal and consists of two halves – the cavity and the core. The design and precision of the mold significantly affect the quality of the final product.
4. Cooling System
Once the plastic is injected, it must cool and solidify. The cooling system, often integrated into the mold, circulates a cooling medium to expedite this process, ensuring that parts are ready for ejection quickly.
5. Ejector System
After the part has cooled, the ejector system pushes the finished product out of the mold. This mechanism is crucial for maintaining production efficiency.
Understanding Mold Design in Injection Molding
Mold design is a critical aspect of injection molding that can significantly impact product quality and production efficiency. Several factors must be considered when designing a mold:
1. Cavity Design
The cavity design dictates the shape and dimensions of the final product. Designers must ensure that the cavity allows for proper flow of the molten plastic and minimizes any potential defects.
2. Draft Angles
Draft angles are incorporated into the mold to facilitate the easy removal of the finished part. Properly designed draft angles minimize friction and reduce wear on the mold.
3. Cooling Channels
Incorporating effective cooling channels within the mold helps to control the temperature during the injection process. This ensures uniform cooling and can reduce cycle times.
4. Gate Design
The gate is the opening through which the molten plastic enters the mold. The design and placement of the gate can influence the flow of material, affecting the overall quality of the part.
Types of Plastic Materials Used in Injection Molding
The selection of plastic materials is crucial in the injection molding process. Different types of plastics offer unique properties that can enhance the performance and suitability of the final product.
1. Thermoplastics
Thermoplastics are the most commonly used materials in injection molding. They can be melted multiple times without significant degradation, making them versatile for various applications. Examples include polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP).
2. Thermosetting Plastics
Unlike thermoplastics, thermosetting plastics harden permanently after being set. They are known for their durability and heat resistance, making them suitable for specialized applications. Examples include epoxy and phenolic resins.
3. Bioplastics
With the rising demand for sustainable manufacturing, bioplastics have gained popularity. These materials are derived from renewable sources and can be used in various applications without compromising performance.
The Injection Molding Process Explained
Understanding the injection molding process is essential for anyone interested in manufacturing. The process can be broken down into several key steps:
1. Material Preparation
The process begins with the preparation of raw plastic materials, which are dried and fed into the injection unit.
2. Melting
The plastic granules are heated in the barrel, where they are melted into a viscous liquid by the rotating screw.
3. Injection
Once sufficiently melted, the molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure.
4. Cooling
After filling the cavity, the molten plastic is allowed to cool, solidifying into the desired shape.
5. Ejection
Once cooled, the ejector system pushes the finished part out of the mold, completing the cycle.
Recent Advancements in Injection Molding Technology
As technology evolves, so does the injection molding process. Recent advancements have enhanced efficiency, precision, and sustainability.
1. 3D Printing Integration
The integration of 3D printing technology in mold design allows for rapid prototyping and customization, reducing lead times and costs.
2. Smart Manufacturing
The incorporation of IoT (Internet of Things) devices enables real-time monitoring of the injection molding process, allowing manufacturers to optimize production and reduce downtime.
3. Sustainable Practices
Advancements in material sciences have led to the development of eco-friendly plastics, further promoting sustainability in the industry.
4. Improved Automation
Automation technologies, such as robotic arms for part removal and handling, streamline the injection molding process, improving efficiency and safety.
Applications of Injection Molding in Various Industries
Injection molding technology finds applications across a multitude of industries, thanks to its versatility and efficiency.
1. Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, injection molding is used to produce a variety of components, from interior trims to complex engine parts.
2. Consumer Goods
The consumer goods market relies heavily on injection-molded products, including toys, household items, and packaging.
3. Medical Devices
Injection molding is crucial in manufacturing medical devices, as it allows for the production of precise and sterile components.
Challenges in Injection Molding and How to Overcome Them
Despite its advantages, the injection molding process does face challenges that manufacturers must navigate.
1. Material Selection
Choosing the right material for a specific application can be challenging, as it directly affects the performance and durability of the final product.
2. Production Costs
High initial costs for mold design and production can be a barrier for small manufacturers. Utilizing advanced technologies can help reduce these costs over time.
3. Quality Control
Maintaining quality throughout the production process is paramount. Implementing stringent quality control measures can mitigate defects and ensure consistent quality.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of injection molding technology requires a deep understanding of its components, processes, and applications. As advancements continue to shape the industry, manufacturers must stay informed and adaptable. By leveraging the insights provided in this comprehensive guide, professionals can enhance their practices, improve their products, and drive innovation within their organizations.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is injection molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce parts by injecting molten plastic into a mold.
2. What materials are commonly used in injection molding?
Common materials include thermoplastics, thermosetting plastics, and bioplastics.
3. How does the injection molding process work?
The process involves material preparation, melting, injection, cooling, and ejection.
4. What are the benefits of injection molding?
Benefits include high precision, efficiency, and the ability to produce complex shapes.
5. What industries use injection molding?
Injection molding is used in various industries, including automotive, consumer goods, and medical devices.
parts of the injection
Related news
2024-11-15