Understanding Overmolding and Insert Molding: Techniques for Enhanced Manufacturing
Time:
2025-06-19 09:21
Source:
Overmolding and insert molding are two specialized manufacturing processes that play a critical role in the production of complex products within the machining and tooling sector. Understanding these techniques can help professionals optimize their designs, improve product performance, and enhance overall manufacturing efficiency.
**What is Overmolding?**
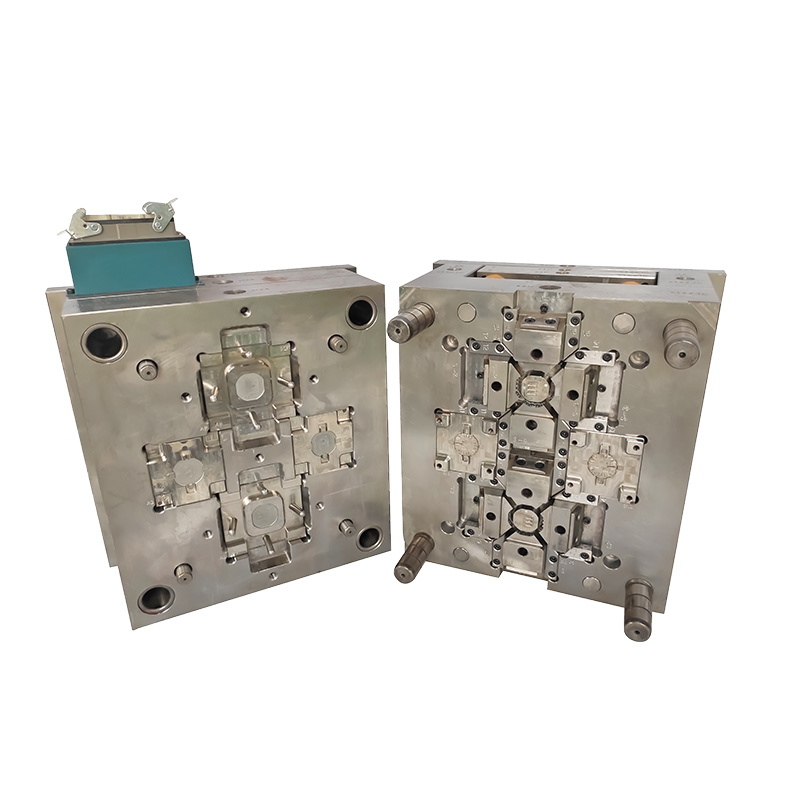
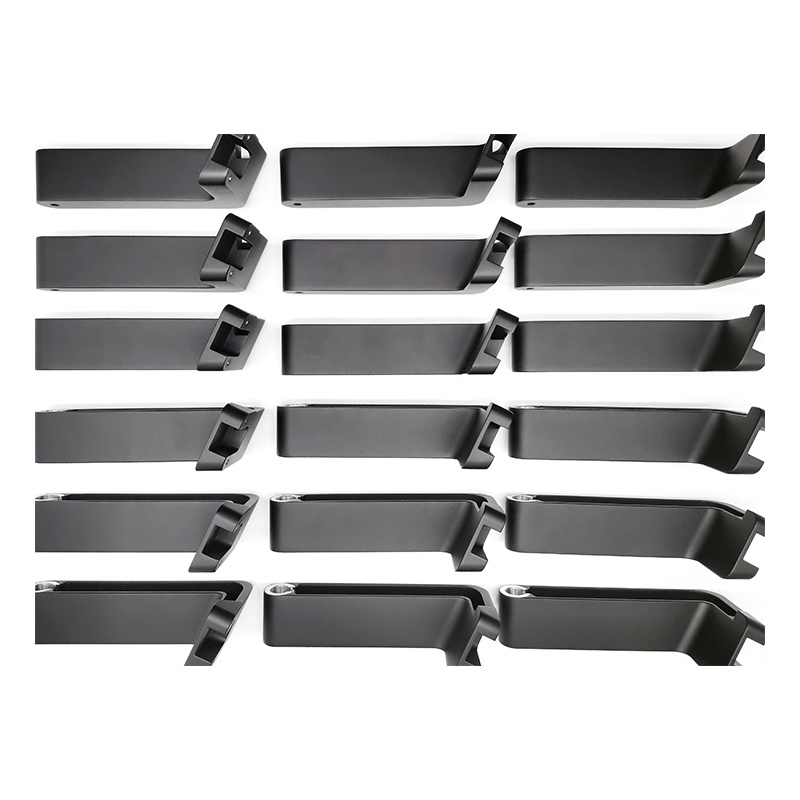
Overmolding involves the process of combining two materials to create a single, cohesive product. Typically, a substrate material (usually plastic or metal) is first molded into a specific shape. Then, a second layer of material—often a softer plastic—is molded over the first material to provide enhanced grip, cushioning, or aesthetic appeal. This technique is particularly popular in the production of consumer electronics, automotive components, and medical devices, where tactile surfaces or enhanced ergonomics are crucial.
One of the key advantages of overmolding is the ability to integrate multiple functionalities into a single product. For instance, by using this technique, manufacturers can create products that are not only more durable but also lighter and more comfortable to use. Additionally, overmolding can significantly reduce assembly time and costs, as multiple parts can be combined into one.
**What is Insert Molding?**
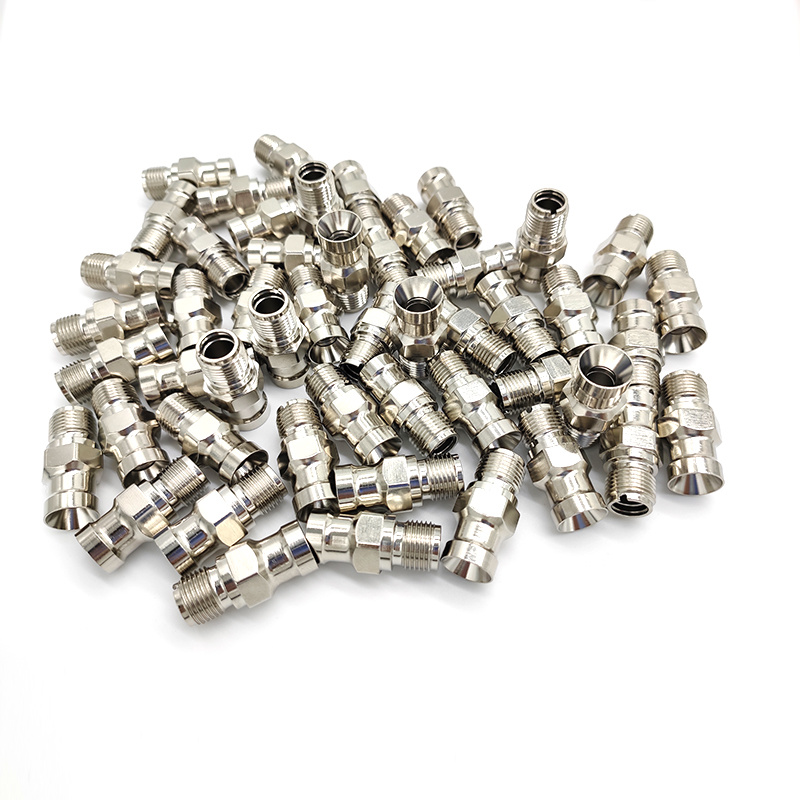
Insert molding, on the other hand, involves the placement of pre-formed components (inserts) into a mold before the primary material is injected. This process allows for the efficient integration of metal or plastic components into a molded part, enhancing the functionality and versatility of the final product. Insert molding is widely used in applications such as connectors, fasteners, and various electronic components.
The benefits of insert molding include improved structural integrity and enhanced performance of the final product. By embedding components directly into the molded part, manufacturers can reduce the need for additional assembly, leading to a more streamlined production process. It also allows for better design flexibility, enabling the incorporation of complex geometries and features that might not be possible with traditional manufacturing methods.
**Considerations for Implementation**
While both overmolding and insert molding provide significant advantages, there are essential factors to consider when implementing these techniques. Material compatibility is critical; selecting the right materials that bond well together ensures optimal performance. Additionally, the design of the mold must accommodate the specific requirements of each process, including the flow of materials and cooling times.
In conclusion, overmolding and insert molding are powerful techniques that can enhance the manufacturing capabilities within the machining and tooling industry. By leveraging these processes, professionals can create innovative, high-performance products that meet the demands of today’s market while improving cost-efficiency and production speed.
**What is Overmolding?**
Overmolding involves the process of combining two materials to create a single, cohesive product. Typically, a substrate material (usually plastic or metal) is first molded into a specific shape. Then, a second layer of material—often a softer plastic—is molded over the first material to provide enhanced grip, cushioning, or aesthetic appeal. This technique is particularly popular in the production of consumer electronics, automotive components, and medical devices, where tactile surfaces or enhanced ergonomics are crucial.
One of the key advantages of overmolding is the ability to integrate multiple functionalities into a single product. For instance, by using this technique, manufacturers can create products that are not only more durable but also lighter and more comfortable to use. Additionally, overmolding can significantly reduce assembly time and costs, as multiple parts can be combined into one.
**What is Insert Molding?**
Insert molding, on the other hand, involves the placement of pre-formed components (inserts) into a mold before the primary material is injected. This process allows for the efficient integration of metal or plastic components into a molded part, enhancing the functionality and versatility of the final product. Insert molding is widely used in applications such as connectors, fasteners, and various electronic components.
The benefits of insert molding include improved structural integrity and enhanced performance of the final product. By embedding components directly into the molded part, manufacturers can reduce the need for additional assembly, leading to a more streamlined production process. It also allows for better design flexibility, enabling the incorporation of complex geometries and features that might not be possible with traditional manufacturing methods.
**Considerations for Implementation**
While both overmolding and insert molding provide significant advantages, there are essential factors to consider when implementing these techniques. Material compatibility is critical; selecting the right materials that bond well together ensures optimal performance. Additionally, the design of the mold must accommodate the specific requirements of each process, including the flow of materials and cooling times.
In conclusion, overmolding and insert molding are powerful techniques that can enhance the manufacturing capabilities within the machining and tooling industry. By leveraging these processes, professionals can create innovative, high-performance products that meet the demands of today’s market while improving cost-efficiency and production speed.
overmolding insert molding
Previous Page
Previous Page
Related news
2024-11-15