Building Prototypes with Low Volume Injection Molding: Best Practices for Success
Time:
2025-08-11 13:20
Source:
Building Prototypes with Low Volume Injection Molding: Best Practices for Success
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Low Volume Injection Molding
2. Understanding the Benefits of Low Volume Injection Molding
3. Key Steps in the Prototyping Process
3.1 Initial Design Considerations
3.2 Material Selection for Prototypes
4. Essential Equipment for Low Volume Injection Molding
5. Best Practices for Effective Prototyping
5.1 Optimizing Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
5.2 Efficient Tooling Techniques
5.3 Quality Control Measures
6. Common Challenges and Solutions in Low Volume Injection Molding
7. Case Studies: Successful Prototyping
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
9. Conclusion
1. Introduction to Low Volume Injection Molding
Low volume injection molding is a specialized manufacturing process used primarily for creating prototypes or small quantities of products. Unlike traditional injection molding, which often requires large production runs to be cost-effective, low volume molding allows engineers and designers to quickly produce functional prototypes without the need for mass production setups.
This process is invaluable in the development of products across various industries—including automotive, consumer electronics, and medical devices—where quick iteration and testing are crucial.
2. Understanding the Benefits of Low Volume Injection Molding
Low volume injection molding offers several benefits that make it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to produce prototypes:
- **Cost-Effective**: Lower tooling costs compared to high-volume production molds, making it easier for businesses to bring new products to market.
- **Faster Turnaround Time**: Rapid prototyping capabilities allow for quicker iterations and testing, enabling faster decision-making processes.
- **Flexibility in Design**: Designers can experiment with different materials and designs without the high costs associated with traditional molding methods.
- **Reduced Waste**: More efficient use of materials leads to less waste, contributing to a more sustainable manufacturing process.
3. Key Steps in the Prototyping Process
Creating prototypes using low volume injection molding involves several critical steps that ensure the final product meets the desired specifications and quality standards.
3.1 Initial Design Considerations
The first step in the prototyping process is to finalize the design of the product. This involves:
- Conducting a thorough design review.
- Ensuring that the design is both functional and manufacturable.
- Considering the end-use of the product to determine necessary specifications.
3.2 Material Selection for Prototypes
Choosing the right material is essential. Factors to consider include:
- Mechanical properties required for functionality.
- Compatibility with the chosen injection molding process.
- Cost considerations and availability of materials.
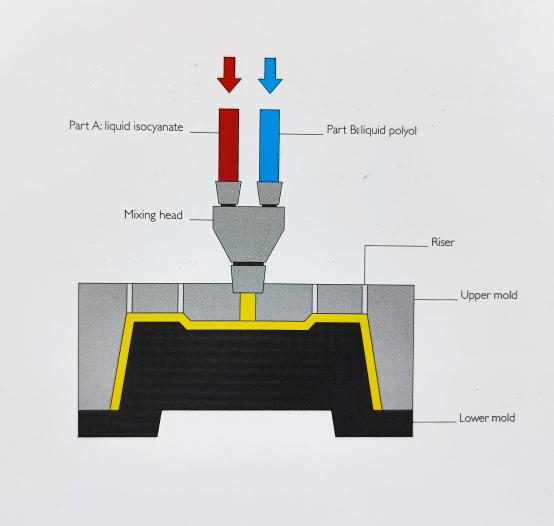
4. Essential Equipment for Low Volume Injection Molding
Effective low volume injection molding requires specific equipment tailored to meet the unique needs of prototype production:
- **Injection Molding Machine**: Suitable for small batch production and capable of handling various materials.
- **Mold Tooling**: Custom molds that can be quickly manufactured or modified for rapid prototyping.
- **Cooling Systems**: Efficient cooling systems are crucial for maintaining consistent quality and reducing cycle times.
5. Best Practices for Effective Prototyping
To maximize the benefits of low volume injection molding, it's important to follow best practices throughout the prototyping process.
5.1 Optimizing Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
Designing with manufacturability in mind can significantly reduce production costs and lead times. Key considerations include:
- Simplifying complex geometries where possible.
- Ensuring uniform wall thickness to avoid issues during molding.
- Designing features that facilitate easy ejection from the mold.
5.2 Efficient Tooling Techniques
Utilizing efficient tooling techniques can enhance the speed and quality of prototype production:
- Consider using aluminum molds for faster turnaround times and lower costs.
- Employ rapid tooling methods for quicker modifications.
5.3 Quality Control Measures
Implementing rigorous quality control measures throughout the process is essential to ensure that prototypes meet specifications:
- Conduct regular inspections of molds and prototypes.
- Utilize advanced technologies such as 3D scanning to ensure dimensional accuracy.
6. Common Challenges and Solutions in Low Volume Injection Molding
While low volume injection molding is advantageous, several challenges can arise:
- **Limited Material Options**: Not all materials are suitable for low volume runs. Research and select materials appropriately.
- **Tooling Costs**: Initial costs can be high, but careful planning and efficient design can mitigate these expenses.
- **Production Consistency**: Variability in production quality can occur; maintaining strict quality control can address these issues.
7. Case Studies: Successful Prototyping
Several companies have successfully utilized low volume injection molding to bring innovative products to market. For example:
- **Automotive Industry**: A leading car manufacturer used low volume injection molding to prototype components, resulting in reduced time-to-market for their latest vehicle model.
- **Consumer Electronics**: A tech startup implemented low volume molding for a new gadget, allowing them to iterate designs quickly based on user feedback.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
**Q1: What is low volume injection molding?**
Low volume injection molding is a manufacturing process ideal for producing small quantities of parts or prototypes, reducing costs and lead times compared to traditional mass production methods.
**Q2: How long does the prototyping process take?**
The duration of the prototyping process can vary depending on design complexity and material selection, but low volume injection molding typically allows for faster turnaround times than traditional methods.
**Q3: What materials can be used in low volume injection molding?**
Common materials include thermoplastics such as ABS, polycarbonate, and nylon, as well as rubber-like materials for flexible prototypes.
**Q4: How do I ensure quality in my prototypes?**
Implementing stringent quality control measures, including regular inspections and utilizing advanced measurement technologies, can ensure high-quality prototypes.
**Q5: Is low volume injection molding suitable for all types of products?**
While low volume injection molding is versatile, it may not be suitable for extremely complex parts or high-performance materials that require mass production.
9. Conclusion
Building prototypes with low volume injection molding is a smart approach for manufacturers seeking to innovate and bring products to market efficiently. By understanding the processes, benefits, and best practices of low volume molding, businesses can leverage this method to optimize their prototyping efforts, reduce costs, and enhance product development. Embracing these strategies will not only lead to successful prototypes but also foster a culture of innovation that can drive long-term success in the competitive manufacturing landscape.
low volume injection molding
Previous Page
Previous Page
Related news
2024-11-15